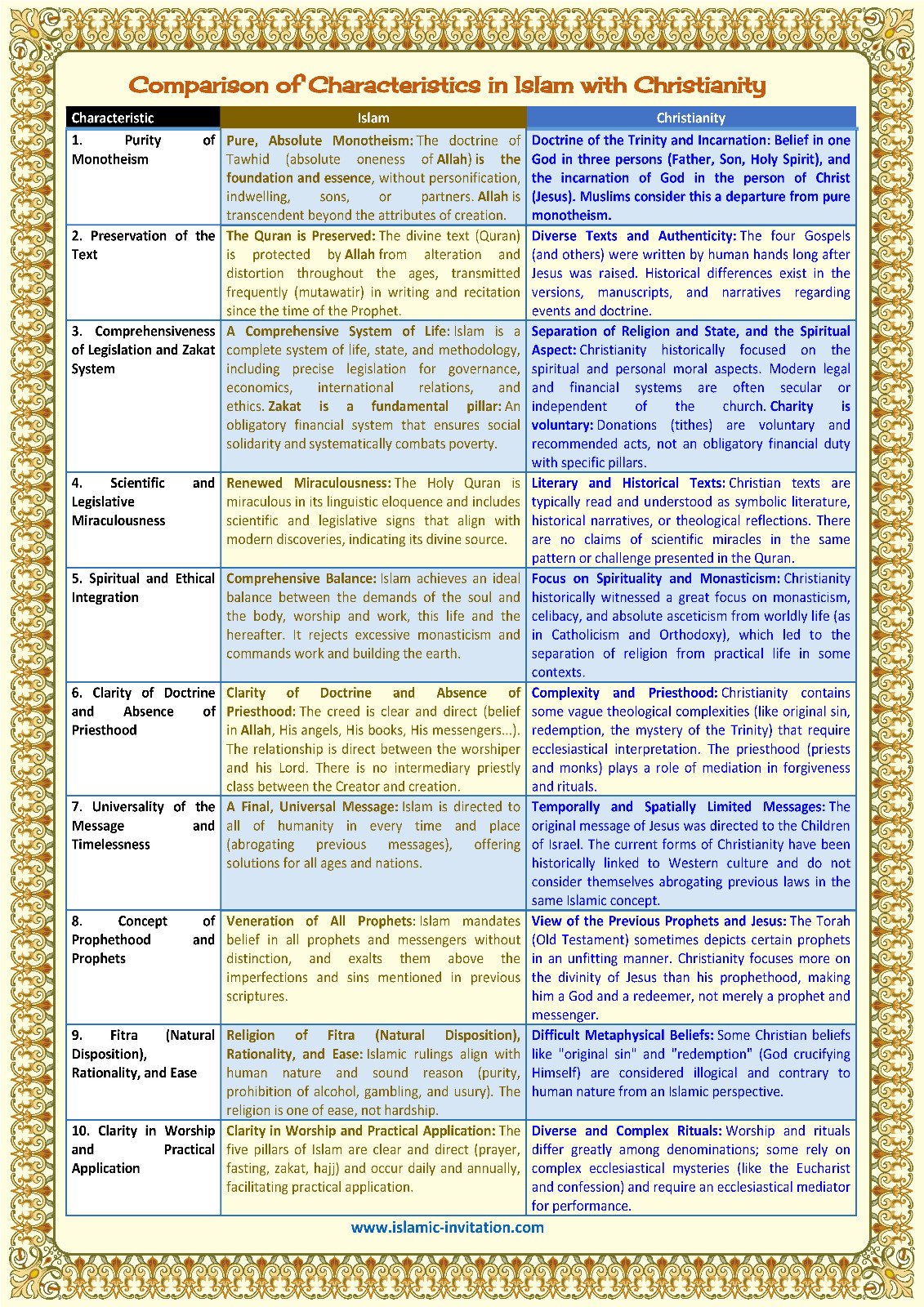
Characteristic
|
Islam
|
Christianity
|
1. Purity of Monotheism
|
Pure, Absolute Monotheism: The doctrine of Tawhid (absolute oneness of Allah) is the foundation and essence, without personification, indwelling, sons, or partners. Allah is transcendent beyond the attributes of creation.
|
Doctrine of the Trinity and Incarnation: Belief in one God in three persons (Father, Son, Holy Spirit), and the incarnation of God in the person of Christ (Jesus). Muslims consider this a departure from pure monotheism.
|
2. Preservation of the Text
|
The Quran is Preserved: The divine text (Quran) is protected by Allah from alteration and distortion throughout the ages, transmitted frequently (mutawatir) in writing and recitation since the time of the Prophet.
|
Diverse Texts and Authenticity: The four Gospels (and others) were written by human hands long after Jesus was raised. Historical differences exist in the versions, manuscripts, and narratives regarding events and doctrine.
|
3. Comprehensiveness of Legislation and Zakat System
|
A Comprehensive System of Life: Islam is a complete system of life, state, and methodology, including precise legislation for governance, economics, international relations, and ethics. Zakat is a fundamental pillar: An obligatory financial system that ensures social solidarity and systematically combats poverty.
|
Separation of Religion and State, and the Spiritual Aspect: Christianity historically focused on the spiritual and personal moral aspects. Modern legal and financial systems are often secular or independent of the church. Charity is voluntary: Donations (tithes) are voluntary and recommended acts, not an obligatory financial duty with specific pillars.
|
4. Scientific and Legislative Miraculousness
|
Renewed Miraculousness: The Holy Quran is miraculous in its linguistic eloquence and includes scientific and legislative signs that align with modern discoveries, indicating its divine source.
|
Literary and Historical Texts: Christian texts are typically read and understood as symbolic literature, historical narratives, or theological reflections. There are no claims of scientific miracles in the same pattern or challenge presented in the Quran.
|
5. Spiritual and Ethical Integration
|
Comprehensive Balance: Islam achieves an ideal balance between the demands of the soul and the body, worship and work, this life and the hereafter. It rejects excessive monasticism and commands work and building the earth.
|
Focus on Spirituality and Monasticism: Christianity historically witnessed a great focus on monasticism, celibacy, and absolute asceticism from worldly life (as in Catholicism and Orthodoxy), which led to the separation of religion from practical life in some contexts.
|
6. Clarity of Doctrine and Absence of Priesthood
|
Clarity of Doctrine and Absence of Priesthood: The creed is clear and direct (belief in Allah, His angels, His books, His messengers...). The relationship is direct between the worshiper and his Lord. There is no intermediary priestly class between the Creator and creation.
|
Complexity and Priesthood: Christianity contains some vague theological complexities (like original sin, redemption, the mystery of the Trinity) that require ecclesiastical interpretation. The priesthood (priests and monks) plays a role of mediation in forgiveness and rituals.
|
7. Universality of the Message and Timelessness
|
A Final, Universal Message: Islam is directed to all of humanity in every time and place (abrogating previous messages), offering solutions for all ages and nations.
|
Temporally and Spatially Limited Messages: The original message of Jesus was directed to the Children of Israel. The current forms of Christianity have been historically linked to Western culture and do not consider themselves abrogating previous laws in the same Islamic concept.
|
8. Concept of Prophethood and Prophets
|
Veneration of All Prophets: Islam mandates belief in all prophets and messengers without distinction, and exalts them above the imperfections and sins mentioned in previous scriptures.
|
View of the Previous Prophets and Jesus: The Torah (Old Testament) sometimes depicts certain prophets in an unfitting manner. Christianity focuses more on the divinity of Jesus than his prophethood, making him a God and a redeemer, not merely a prophet and messenger.
|
9. Fitra (Natural Disposition), Rationality, and Ease
|
Religion of Fitra (Natural Disposition), Rationality, and Ease: Islamic rulings align with human nature and sound reason (purity, prohibition of alcohol, gambling, and usury). The religion is one of ease, not hardship.
|
Difficult Metaphysical Beliefs: Some Christian beliefs like "original sin" and "redemption" (God crucifying Himself) are considered illogical and contrary to human nature from an Islamic perspective.
|
10. Clarity in Worship and Practical Application
|
Clarity in Worship and Practical Application: The five pillars of Islam are clear and direct (prayer, fasting, zakat, hajj) and occur daily and annually, facilitating practical application.
|
Diverse and Complex Rituals: Worship and rituals differ greatly among denominations; some rely on complex ecclesiastical mysteries (like the Eucharist and confession) and require an ecclesiastical mediator for performance.
|